How Walmart Used Data to Expand Its Delivery Footprint
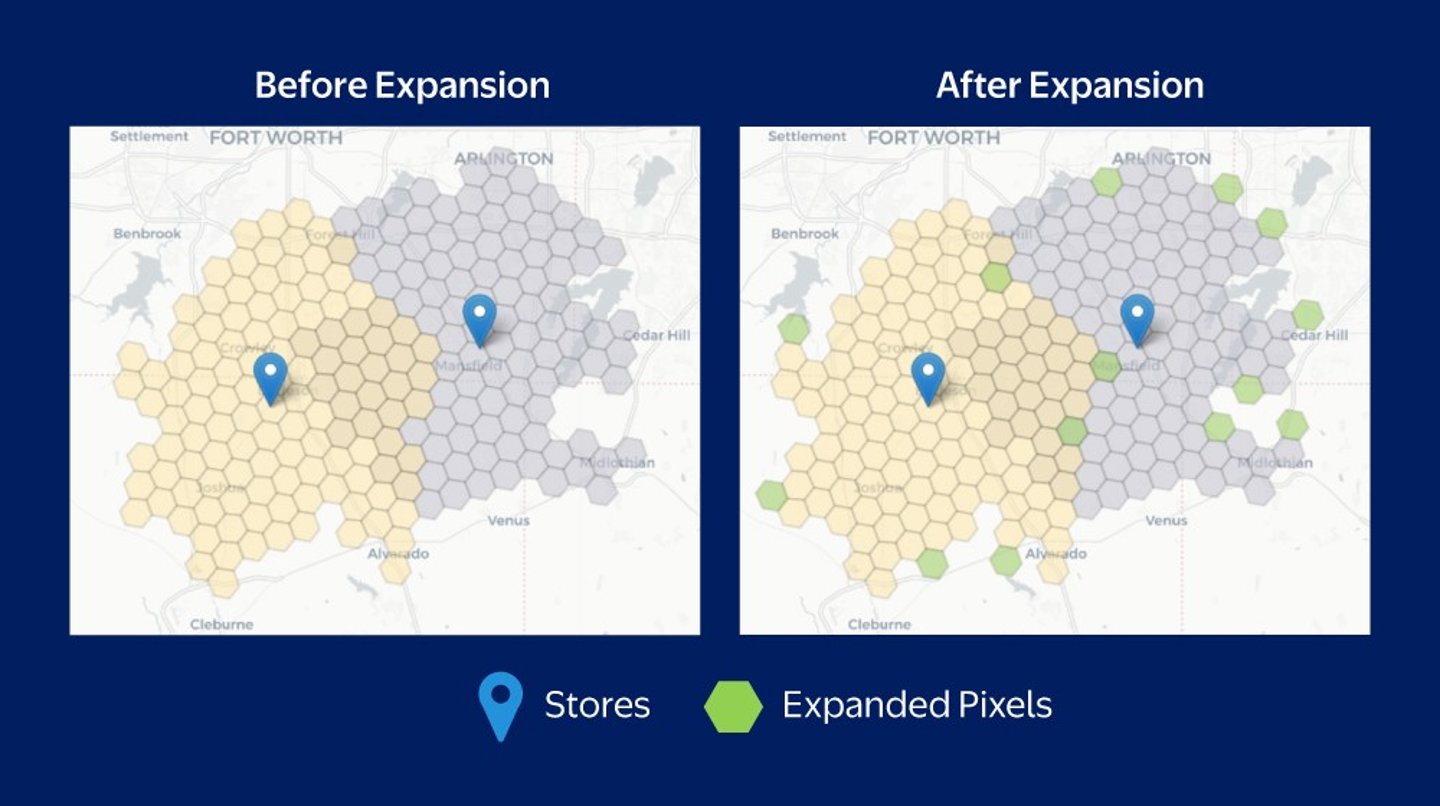
Walmart is investing in innovation to serve more delivery customers – this time with the use of geospatial technology. The data science model allows the retailer to divide geographic areas into precise hexagonal grids instead of relying on traditional boundaries like ZIP codes, which optimizes delivery zones for greater efficiency.
By dividing large areas into smaller, more precise hexagonal grids that cover entire spaces without leaving gaps, Walmart has been able to adjust delivery zones with greater accuracy. The move has helped the retailer expand its delivery service to 12 million more households across the U.S.
“For example, a household that might have previously been just beyond the delivery boundary, now can enjoy the same convenient service as their neighbors across the street,” Walmart explained in a blog post. “By shifting from rigid mapping methods to a more data-driven model, we ensure more customers have access to our delivery offerings.”
[RELATED: AI-Driven Robot Debuts at Georgia Walmart’s Restaurant]
Additionally, the geospatial technology will allow delivery orders to be fulfilled by multiple Walmart stores within a shopper’s service area. This way, if one store doesn’t have a particular item but another nearby location does, Walmart delivery drivers can pick up products from both stores.
Each week, approximately 270 million customers and members visit Walmart’s more than 10,750 stores and numerous e-commerce websites in 19 countries. With FY2025 revenue of $681 billion, the company employs approximately 2.1 million associates worldwide. Bentonville, Ark.-based Walmart U.S. is No. 1 on Progressive Grocer’s 2024 list of the top food and consumables retailers in North America.